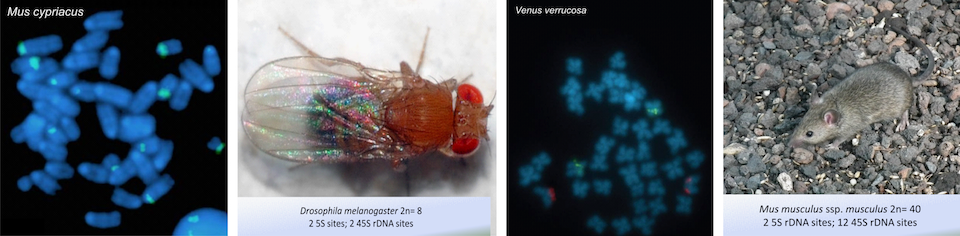
Select output fields
| Phyllum | Class | Order | Popular name | ||
| Family | Genus | Specific epithet | Specific authority | Infraspecific category | |
| 2C mean1(pg) | 2C mean1(mbp) | 2C range1 pg | |||
| Chromosome number (2n) | Ploidy level | ||||
| Number of 5S signals | Range of 5S signals | Position2 of 5S signals (5S P) | |||
| Number of 45S3 signals | Range of 45S signals | Position2 of 45S signals (45S P) | Arrangement | ||
| Autosome or sex chromosome | 5S chrom. type | ||||
| Sex chrom. number | 45S chrom. type | ||||
| B chromosomes | Ag-NOR | ||||
| Original reference | |||||
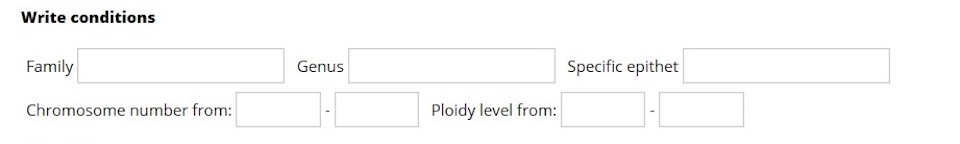
Write conditions
| Phyllum Class Order | |||||
| Family Genus Specific epithet | |||||
| Popular Name | |||||
| Chromosome number from: - Ploidy level from: - |
Select filters
| Sort by |
Show |
||||
For help with searching and querying the database, go to HELP
1 source: Animal genome size database (http://www.genomesize.com)
2 position refers to interstitial, pericentromeric, distal or occupying whole chromosome arm
3 refers to 45S rDNA (18S-5.8S-26S rRNA genes)
The animalrDNAdatabase has been organized so that you can make either a Simple or an Advanced Search.
The Simple Search is basic and aimed to obtain easily fast results. You only have to type the name of the family, genus, species or even specific epithet of your interest in the Search Box and the results will automatically be displayed.
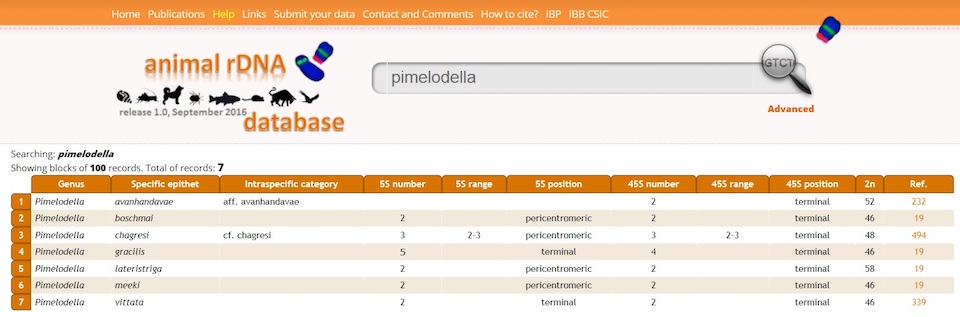
By default, the information that will appear in this type of search, besides chromosome number, is: number, range and position of 5S and 45S signals and ID number of the source publication (Ref.) whose complete name will appear by moving your cursor over it. The total number of records for your search is shown at the right top of the results. A given Simple Search can be later refined by clicking in the Advanced Search and selecting any of the available options.
NOTE: With some of the type genera of families, those that have left their complete name for the name of the family, when typing their names, information on data of the full family will appear.This can be avoided by clicking once the space bar after the name of the genus.
The Advanced Search allows different options to refine your search. You can access from any tab of the webpage by clicking the word ‘Advanced’ highlighted in bold. Then a query form will appear.
In the first section of the query form you can select, by clicking in the corresponding box, all the output fields that you want in your search record. There are some options ticked by default (explained at the Simple Search).
Therefore, if you want additional information then click in the appropriate boxes and these data will be shown if available:

The second section allows you writing conditions, where it can be chosen that only results for a given family, genus or species are shown. Also, you can choose that your search only presents results for (a) given ploidy level(s) and chromosome number(s).
Finally, the third section enables to apply filters to your search. There is a last option that permits to sort the results by family, genus, species, genome size, chromosome number or ploidy level; as for the previous filters, the appropriate choice has to be selected from the drop-down box under the option 'Sort by' at the bottom of the query form. The results of searches are automatically sorted by alphabetical order.

Once the different options are chosen, click the ‘Search’ button at the right bottom of the query form. To perform subsequent advanced searches you can refresh the query form by clicking the ‘Delete’ button at the right top of the form.
The positions of rDNA signals in chromosomes have been reduced to only three different options for the sake of clarity. These are:
Only the most abundant position has been selected to characterize each kind of rDNA loci, although in some species there may be more than one possible location. The source publication should always be consulted in case of doubt.
Exceptionally, we have used the terms “some” or “several” when the number of signals was not determined by the source publication and was impossible to ascertain.